A general purpose cleaner is used to clean multiple surfaces in household, industrial or institutional applications. Different kinds of chemical cleaners are formulated for the cleaning of dirt, grime, and germs from windows, floors, countertops and appliances. General-purpose cleaners are versatile solutions designed to clean multiple surfaces and address various cleaning challenges. But what exactly makes these cleaners so effective? In this article, we’ll explore the ingredients that power general-purpose cleaners and examine how they work to keep our environment clean and hygienic.
Surfactants: The Cleaning Powerhouses

At the heart of every general purpose cleaner are surfactants, which are short for surface-active agents. These are the key ingredients responsible for breaking down dirt and grease, allowing them to be easily rinsed away Common surfactants found in general purpose cleaners include alkyl sulfates, alkyl ethoxylates, and quaternary ammonium compounds.
These highly versatile compounds are amphiphilic molecules with hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts, reducing surface tensions by aligning at interfaces like air-water or oil-water. They’re categorized by their polar head, with non-ionic, anionic, cationic, and zwitterionic types, with anionic and non-ionic being the most common. Anionics are prevalent in cleaning products, while nonionics are used in wetting agents and food. Surfactants’ absorption at interfaces disrupt cohesive forces, lowering surface tension and forming micelles at high concentrations.
Solvents: Dissolving Stubborn Stains

Solvent cleaners are highly effective solutions for industrial cleaning, breaking down oils and grease into smaller particles for easy removal. Solvents are vital in cleaning by dissolving stains and soil particles, ensuring surfaces remain residue-free. They come in various potencies, ranging from mild to strong, and are favoured for their versatility. Common types of solvent cleaners include oxygenated hydrocarbon and halogenated solvents. Oxygenated solvents, like alcohols and glycol ethers, boast high purity levels due to rigorous refinement processes. Hydrocarbon solvents penetrate hard-to-reach areas without leaving behind water, preventing rust formation. Halogenated solvents containing elements like chlorine or bromine excel at removing flux from circuit boards and degreasing metal parts. They are found in various cleaning products and serve multiple purposes beyond stain removal, such as stabilizing solutions, adjusting viscosity, and promoting faster drying for streak-free surfaces.
Chelating Agents: Preventing Hard Water Deposits

Hard water minerals like calcium and magnesium can leave behind unsightly deposits on surfaces, making them appear dull and dirty. Chelating agents help prevent the buildup of hard water deposits by binding to these minerals and keeping them in solution. Common chelating agents used in general-purpose cleaners include citric acid, EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), and phosphates. By sequestering hard water minerals, chelating agents ensure surfaces remain clean and shiny after cleaning.
pH Adjusters: Balancing Cleaning Power
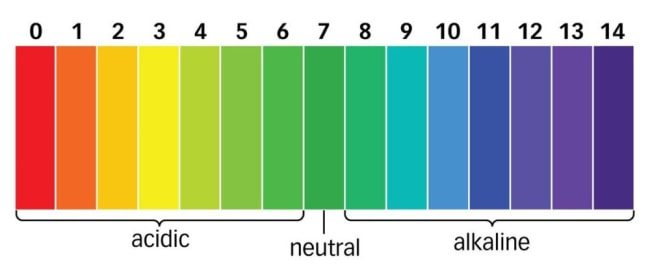
The pH level of a cleaner plays a crucial role in its effectiveness on different types of soils and surfaces. pH adjusters are ingredients that help maintain the optimal pH balance for cleaning. For example, alkaline cleaners with a high pH are effective at removing greasy soils, while acidic cleaners with a low pH are better suited for dissolving mineral deposits and soap scum. Common pH adjusters used in general-purpose cleaners include sodium hydroxide (lye) for alkaline cleaners and citric acid for acidic cleaners.
Fragrances and Dyes: Enhancing the Cleaning Experience

While not essential for cleaning performance, fragrances and dyes are often added to general-purpose cleaners to enhance the user experience. Fragrances help mask unpleasant odours and leave behind a fresh scent after cleaning, while dyes provide visual appeal and help consumers distinguish between different products.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
Conclusion: General Purpose Cleaner
In conclusion, the efficacy of all-purpose cleaners lies in their carefully formulated ingredients, each playing a vital role in achieving cleanliness and hygiene. Surfactants, as the cleaning powerhouses, break down dirt and grease, while solvents dissolve stubborn stains, and chelating agents prevent hard water deposits. pH adjusters balance cleaning power, ensuring optimal performance across various surfaces, while fragrances and dyes enhance the overall cleaning experience. Understanding these ingredients illuminates the science behind effective cleaning practices, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment for all.