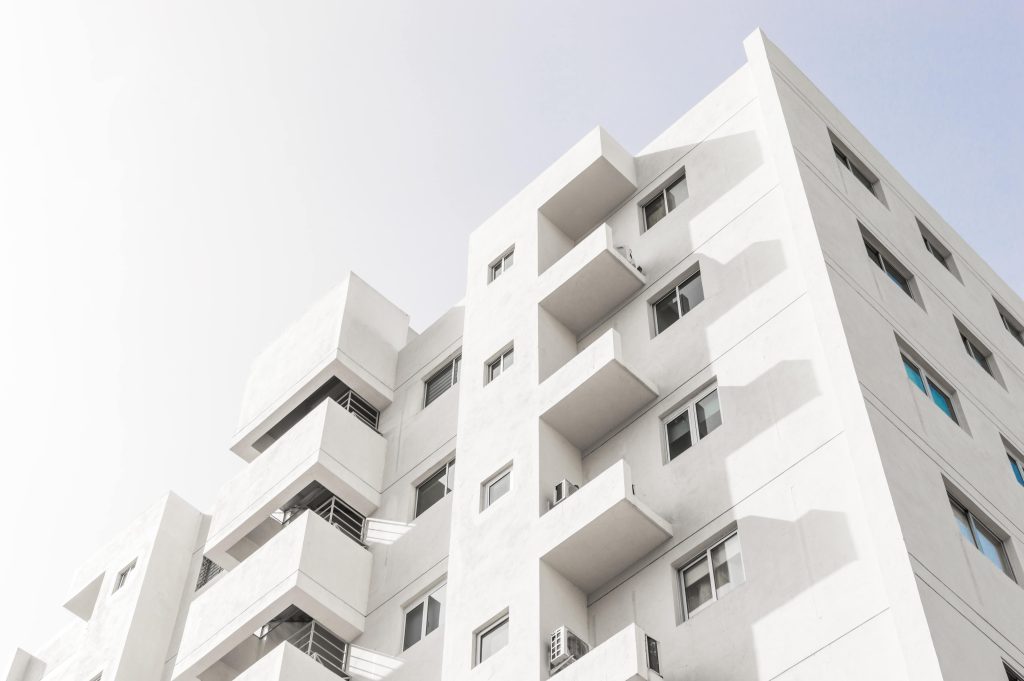
Living in Southeast Asia, the hot and humid climate can affect buildings’ facades, stability, and safety. ASHRAE Humidity Standards recommend maintaining humidity below 60%, but tropical countries like Singapore and Thailand can reach 70-90% humidity. This high humidity leads to moss and algae formation, causing structural damage. Water and dissolved salts can also penetrate, leading to cracks and spalling. Seaside bridges are particularly vulnerable to corrosion, undermining their stability. Our article highlights the importance of protective coatings for buildings and offers the best solution for protecting structures from these issues.
Importance of Protective Coatings for Buildings
Protective coatings for buildings for outdoor buildings are necessary for several reasons. We discuss some of them below:
Protection Against Moisture

One of the primary concerns associated with water intrusion is the potential for rot. When water seeps into the building’s structure, it can cause wood and other organic materials to decay. Additionally, moisture creates an ideal environment for mould and mildew growth; weather coatings such as waterproof paints or sealants make the building surfaces resistant to water penetration. As a result, the risk of rot, mould growth, and subsequent structural damage is significantly reduced.
Protective coatings for buildings are particularly important in areas with heavy rainfall or high humidity. By providing an additional layer of defence against water intrusion, protective coatings for buildings help to extend the lifespan of the building’s materials, reducing the frequency and cost of repairs and replacements.
Resistance to UV Rays
Continuous exposure to UV rays can cause fading and discolouration of surfaces. As a result, painted exteriors may lose their vibrancy, and vibrant colours can become dull and washed out over time. Additionally, UV rays can lead to the degradation of materials such as wood, plastics, and synthetic coatings. These materials may become brittle, crack, or experience structural damage.
Protective coatings for buildings with UV protection are designed to mitigate these damaging effects. They incorporate additives or pigments that reflect or absorb UV radiation, minimising fading, discolouration, and degradation. Reflective coatings bounce back some UV rays, reducing the amount penetrating the surface. On the other hand, absorption coatings absorb the UV rays, preventing them from reaching the materials beneath. UV-resistant weather coatings are especially valuable in areas with high levels of solar radiation or regions where intense sunlight is prevalent.

Thermal Insulation

Thermal insulation coatings are designed to help regulate the temperature inside the structure, providing both energy efficiency and comfort advantages.
In hot weather, insulating coatings deflect a considerable amount of the sun’s heat, thus preventing it from penetrating the building. Conversely, in colder climates, insulating weather coatings offer an extra layer of insulation to the structure, aiding in the retention of generated heat indoors. This reduces the need for air conditioning or heating systems, resulting in substantial reductions in energy consumption for cooling or heating. Consequently, utility bills are lowered, environmental impact is minimised, and indoor temperatures remain comfortably regulated even in extreme weather conditions.
Insulating protective coatings for buildings coatings can also help to create a more consistent and comfortable indoor environment year-round. By reducing heat transfer through the building envelope, they help to minimise temperature fluctuations and drafts, improving occupant comfort.
The thermal insulation properties of weather coatings are particularly beneficial for structures such as outdoor offices, warehouses, or residential buildings where temperature control is essential.
Protection Against Pollutants
Outdoor buildings are constantly exposed to various air pollutants, ranging from dust and dirt particles to pollutants emitted from industrial areas or vehicles. These pollutants can settle on the surfaces of the building, leading to unsightly buildup and potential damage. Protective coatings for buildings act as a protective barrier, preventing pollutants from directly contacting the building’s surfaces. The coatings create a smooth and sealed layer that resists the adherence of dirt, dust, and other particles.
Furthermore, weather coatings can also offer chemical resistance, protecting the building against pollutants such as acids, solvents, or corrosive substances. This is particularly important in areas with heavy industrial activity or proximity to chemical-intensive environments.

By acting as a protective barrier, protective coatings for buildings help to reduce the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance of the building. The smooth and sealed surface the coatings provides makes cleaning easier, as dirt and pollutants are less likely to adhere firmly. Regular rainfall or occasional washing can easily remove the accumulated dirt, restoring the building’s appearance.
Enhanced Durability

Protective coatings for buildings create a protective layer that shields the underlying surfaces from various forms of physical damage, resulting in improved longevity and overall structural integrity.
One of the primary ways protective coatings for buildings enhance durability is by providing a barrier against scratches, abrasions, and impact. Outdoor buildings are exposed to potential sources of damage, such as accidental impacts, harsh weather conditions, or contact with objects. The protective layer created by weather coatings acts as a shield, absorbing and dispersing the impact energy. This feature of weather coatings helps to prevent scratches, dents, or other forms of physical damage to the building’s surfaces.
Protective coatings for buildings reduces the deterioration and degradation rate, allowing the materials to withstand the test of time and reducing the need for frequent repairs, replacements, or costly maintenance, especially for structures where visual appeal plays a significant role, such as commercial buildings, public spaces, or residential exteriors.
Aesthetic Appeal
Aesthetic appeal is a significant aspect of protective coatings for buildings for outdoor buildings. These coatings offer a wide range of colours, finishes, and customization options, allowing for enhanced visual appearance and the ability to tailor the building’s look to specific preferences and requirements.
Conclusion: Protective Coatings for Buildings
In conclusion, protective coatings for buildings are vital for addressing challenges in Southeast Asia’s hot and humid climate. They protect against moisture, UV rays, pollutants, and physical damage while enhancing durability and aesthetics. By creating a waterproof barrier, these coatings prevent rot, mould, and structural damage. They also resist fading and degradation from UV rays, regulate indoor temperatures, and minimise cleaning needs. Weather coatings shield surfaces, extend material lifespan, and offer customisation options. Investing in weather coatings ensures long-term stability, safety, and visual appeal for outdoor buildings in this climate.