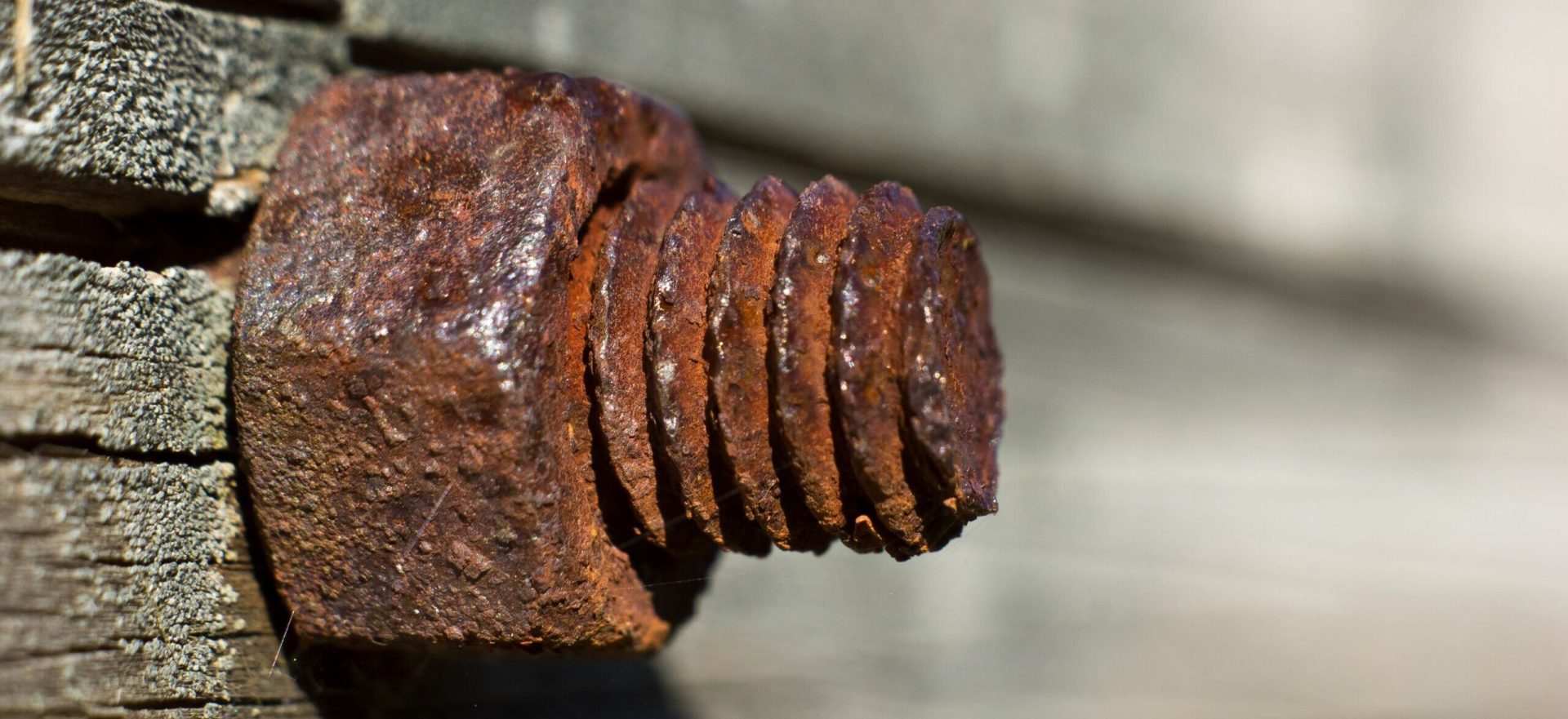
What Are Penetrants?
Penetrants, also known as penetrating oils or, fluids or release agents, are low-viscosity lubricants designed to penetrate and loosen tight, rusted, or corroded parts such as bolts and nuts. They work by seeping into microscopic gaps and crevices, breaking down rust and corrosion, and providing lubrication to reduce friction between metal parts. Commonly used in industrial maintenance and repair, penetrants are effective for loosening fasteners, cleaning surfaces, and preventing rust, although they often require reapplication for ongoing protection.
Composition of Penetrants

Penetrants are carefully formulated to achieve their specific function of loosening and lubricating tight, rusted, or corroded parts. Their composition typically includes:
Base Oil
Function
The base oil serves as the primary lubricating component in penetrants. It provides the essential lubrication needed to reduce friction between moving parts once the penetrant has seeped into the targeted area.
Types
Base oils can be mineral oils derived from crude oil, synthetic oils created through chemical processes, or a blend of both. The choice of base oil affects the penetrant’s overall performance, including its lubrication properties and temperature stability.
Solvents
Function
Solvents are critical in reducing the viscosity of the penetrant, making it thin enough to penetrate into very tight spaces and crevices between metal parts. This penetrating ability is what distinguishes penetrants from other types of lubricants.
Types
Solvents such as mineral spirits, kerosene, acetone, or other petroleum-based liquids are commonly used. They act quickly to break down rust and other deposits, facilitating the movement of the base oil into the crevices.
Additives
Corrosion Inhibitors
These additives help to remove moisture from metal surfaces, which is crucial for preventing rust formation and ensuring effective lubrication.
Water Displacers
Solvents such as mineral spirits, kerosene, acetone, or other petroleum-based liquids are commonly used. They act quickly to break down rust and other deposits, facilitating the movement of the base oil into the crevices.
Other Chemicals
Depending on the specific application, penetrants may also include other additives like anti-wear agents, extreme pressure additives, or detergents. These can improve the penetrant’s ability to clean surfaces, protect against wear and tear, and perform under high-stress conditions.
How They Work

Penetration
Penetrants have low viscosity, meaning they are thin and fluid, which allows them to easily flow into tiny gaps and crevices between metal parts. Combined with their high capillary action, this property enables the penetrant to reach areas that thicker lubricants cannot. As a result, penetrants can effectively penetrate into the tight spaces where rust and corrosion have caused parts to seize, making them essential for loosening fasteners like bolts and nuts in industrial maintenance.
Lubrication
Once the penetrant has seeped into the tight spaces, it lubricates the metal surfaces. This lubrication reduces the friction between moving parts, which prevents further wear and tear. By minimizing friction, the penetrant helps the parts move more freely, making it easier to loosen components stuck due to rust, corrosion, or dirt buildup.
Loosening Rust and Corrosion
Penetrants are equipped with solvents and additives designed to break down rust and corrosion. These solvents dissolve the bonds that hold rust and other deposits in place, effectively loosening the grip that these substances have on metal parts. As the rust and corrosion are broken down, the penetrant makes it easier to free seized components, restoring the functionality of machinery and equipment without the need for excessive force.
Renovating Grimy Industrial Surfaces
In addition to loosening fasteners and freeing up corroded parts, penetrants are also highly effective at cleaning and renovating grimy industrial surfaces. Their powerful solvents cut through layers of dirt, grease, and oil that accumulate on machinery, floors, and equipment in environments such as automotive repair shops, truck terminals, aircraft hangars, meat packing plants, and manufacturing facilities. By breaking down these stubborn residues, penetrants help restore the cleanliness and functionality of industrial areas, improving safety and operational efficiency.
Removing Flammable Hazards
One of the critical safety benefits of using penetrants is their ability to remove flammable hazards caused by grease and oil build-up. Excess grease and oil can pose significant fire risks in industrial settings, mainly when accumulated near heat sources or electrical components. Penetrants dissolve and remove these hazardous residues, reducing the potential for fires and making work environments safer for employees. This preventative measure is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance and safeguarding equipment and workers.
Applications in Industrial Maintenance
Loosening Fasteners
Penetrants are widely used in industrial maintenance for loosening rusted or corroded fasteners such as bolts, nuts, and screws. Over time, exposure to moisture and the elements can cause these components to rust and corrode, making them difficult to remove. Penetrants work by seeping into the threads and breaking down the rust, corrosion, and debris that are causing the fasteners to seize. By reducing the friction and dissolving the bonds between the metal surfaces, penetrants make it easier to loosen these fasteners without damaging the surrounding material or requiring excessive force.
Cleaning
In addition to loosening fasteners, penetrants are effective cleaning agents in industrial settings. They displace water, dirt, and other contaminants from metal surfaces, helping to clean and prepare them for further maintenance or repair. The solvents in penetrants dissolve grease, oil, and other residues, leaving the surfaces clean and free from substances that can lead to corrosion or hinder the performance of machinery. This cleaning capability is particularly valuable in environments where maintaining clean and functional equipment is critical to operations.
Preventive Maintenance
Penetrants play a crucial role in preventive maintenance by being applied to metal surfaces to protect against rust and corrosion. Regular application of penetrants can create a protective barrier that shields the metal from moisture and other corrosive elements. This preventive measure extends the lifespan of equipment and components by reducing the likelihood of rust and corrosion forming in the first place. By keeping metal surfaces lubricated and protected, penetrants help maintain the efficiency and reliability of machinery, reducing the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Machinery Repair
During machinery repair and maintenance, penetrants are invaluable for disassembling parts that have become stuck due to rust, corrosion, or dirt buildup. These fluids penetrate into tight spaces and joints, breaking down the substances that cause parts to seize. This makes it easier to disassemble machinery without damaging the components or requiring excessive effort. Whether it’s removing a rusted bearing, freeing a stuck valve, or disassembling a corroded joint, penetrants help streamline the repair process, saving time and reducing the risk of damage to the machinery.
Qualities of a Penetrant

Versatility
A good penetrant should be versatile, meaning it can be effectively used across various surfaces and applications. It should perform well on various materials, including metals, plastics, and painted surfaces, and be suitable for tasks ranging from removing grease and grime from engines and machinery to cleaning delicate surfaces like painted walls. This adaptability makes it a valuable tool in different industrial settings.
Powerful Cleaning Action
A penetrant should be powerful enough to tackle tough industrial cleaning tasks. It needs to quickly liquefy and emulsify dirt, grime, oil, and grease, ensuring efficient removal of these substances. This powerful cleaning action is essential for restoring the functionality of machinery and maintaining cleanliness in industrial environments.
Lubrication
Effective lubrication is a critical quality for a penetrant. It should reduce friction between moving parts, preventing further wear and tear, and making it easier to disassemble components that have become stuck. Lubrication not only aids in loosening rusted or corroded parts but also helps maintain the overall functionality of machinery.
Emulsification
A high-quality penetrant should have strong emulsifying properties, meaning it can break down and suspend oils, grease, and other contaminants in a liquid form, making them easier to clean and remove. Emulsification ensures that the penetrant can effectively clean surfaces and prepare them for further maintenance or repair.
Corrosion Inhibition
An important quality of a penetrant is its ability to protect metal surfaces from corrosion. It should contain inhibitors that reduce the risk of rust and corrosion, particularly in iron and steel. This feature not only helps in loosening parts but also in preserving the integrity of the equipment over time.
Safety and Environmental Friendliness
Safety is a key consideration, so a penetrant should be non-toxic, non-flammable, and free from hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or chlorinated solvents. Additionally, being biodegradable is a significant advantage, as it reduces the environmental impact and aligns with modern sustainability practices.
Concentrated and Economical
A high-quality penetrant should be concentrated to maximize efficiency and reduce the amount of product needed for effective results. This concentration helps save on storage space and costs, making the penetrant more economical for large-scale industrial applications.
Ease of Use
Finally, a penetrant should be easy to use, providing the benefits of a solvent while maintaining the safety of water-based solutions. This combination allows for quick and efficient application, saving labor and time, essential in fast-paced industrial environments.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
Conclusion
In conclusion, penetrants provide effective solutions for loosening rusted or corroded fasteners, cleaning surfaces, and preventing future corrosion. Their low viscosity and penetrating ability enable them to reach tight spaces, break down rust, and lubricate metal parts, making it easier to maintain and repair equipment. With the added benefits of cleaning action and corrosion inhibition, penetrants are indispensable in various industries, enhancing equipment longevity and operational efficiency.