Anti-seize compound products have emerged as vital solutions in mechanical assemblies and fastening systems. These versatile substances are crucial in preventing galling, seizing, and corrosion while ensuring smooth operations and facilitating easy disassembly. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept of anti-seize, its various forms, such as pastes, greases, and coatings, and the importance of selecting the right product for specific systems. We will also delve into the practical aspects of using anti-seize, providing guidance on proper application techniques and best practices. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of anti-seize and its significance in maintaining the integrity and longevity of clamped interfaces in mechanical systems
What Does Anti-Seize Compound Mean?

Anti-seize refers to substances that protect and lubricate bolts, fasteners, flanges, and similar clamped interfaces. Their primary purpose is to prevent galling, seizing, and corrosion while facilitating easy disassembly.
Anti-seize compounds come in different forms, such as pastes, greases, and coatings. They are formulated using materials like copper and nickel, among others, to cater to specific systems or applications. It is essential to choose the appropriate anti-seize product carefully, considering the specific requirements of the system in question.
What Are the Reasons to Use Anti Seize?
Utilising carefully selected and properly applied anti-seize products can yield a wide array of benefits for engineering systems. Anti-seize serves the following purposes:
- Prevents pick-up and galling of fasteners during the assembly process, ensuring smooth and efficient installation.
- Facilitates the achievement of a more precise and consistent clamping load in fasteners, contributing to enhanced reliability and performance.
- Acts as a lubricant, effectively separating and lubricating the surfaces of jointed interfaces during operation. This reduces wear and the risk of loosening over time.
- Guards against corrosion of interfaces by creating a protective barrier, preventing water ingress and chemical attack that can degrade the integrity of the components.
- Streamlines dismantling procedures and safeguards against component damage during disassembly, making maintenance and repairs more efficient.
Moreover, certain anti-seize products are specifically formulated for dynamic systems, providing additional advantages:
- Assists in the assembly of interference fits, facilitating the joining of components with tight tolerances.
- Reduces fretting wear of components in vibrating systems, minimising the potential for damage caused by repetitive motion.
- Diminishes friction and wear between mated surfaces that undergo relative motion, such as splines and couplings, resulting in improved durability and longevity.
By employing anti-seize products that align with the specific requirements of a system, engineers and technicians can mitigate issues related to assembly, operation, corrosion, and maintenance, thereby enhancing the overall performance and lifespan of critical components.
What Are the Applications of Anti-Seize?

When the need arises, it is recommended to apply a thin layer of anti-seize to each interface within an assembly, ensuring optimal protection for the interfaces involved. Specifically, when using anti-seize on a fastener assembly – anti seize for bolts, it should be applied to the following surfaces:
- The thread of the bolt or stud.
- Plain, unthreaded sections of the bolt or stud if they will be inside the assembly.
- The surface beneath the bolt head.
- The face of the nut.
- All parts of the washer, if one is being used.
It is important to note that a thin layer is sufficient for the effective application of anti-seize. Any excess material will be expelled during the tightening process. By adhering to these guidelines, engineers and technicians can maximise the benefits of anti-seize while ensuring the integrity and longevity of the assembled components and anti seize for bolts.
It is important to note that a thin layer is sufficient for the effective application of anti-seize. Any excess material will be expelled during the tightening process. By adhering to these guidelines, engineers and technicians can maximise the benefits of anti-seize while ensuring the integrity and longevity of the assembled components.
How Much Anti-Seize Compound Should I Apply?
For optimal results, applying a thin layer of anti-seize to the surface in question is generally recommended. In the case of a typical fastener assembly, a film approximately 0.1mm thick is considered suitable.
While some guidance may suggest filling the thread valleys of a bolt with anti-seize, this quantity is often excessive and wasteful. During the tightening process, excess anti-seize will be expelled. Therefore, it is advisable to stick to a thin-layer application thorugh anti seize for bolts.
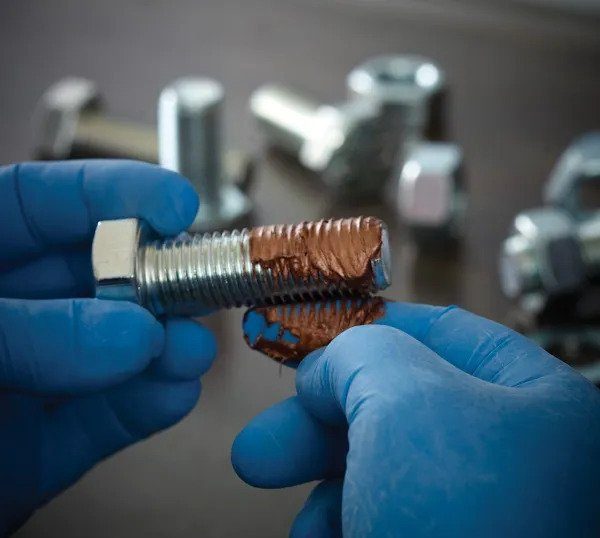

When using an aerosolized anti-seize product, referring to the instructions on the Technical Data Sheet is crucial for achieving a uniform and appropriately thin layer with proper coverage.
However, it is important to note that each system’s specific conditions and requirements should be considered. Factors such as the type of assembly, environmental conditions, and material compatibility may influence the optimal quantity of anti-seize to be applied. Assessing these factors and considering the manufacturer’s recommendations will help ensure the most effective use of anti-seize for a particular application.
What Is the Optimal Technique to Apply Anti-Seize?

To ensure the effective application of anti-seize, it is essential to begin with clean surfaces free from oil, grease, or any other form of contamination. This is particularly important if the components are supplied pre-oiled.
Using a brush is the most effective method for achieving a thin and even layer of anti-seize. It allows for better control and results in a more uniform application, especially when dealing with threads.
It is important to note that a brush should be dedicated to a specific type of material. Once a brush has been used to apply a particular anti-seize compound, it should not be used to apply a different one, even after cleaning. Cross-contamination between anti-seize products can impact their performance.
In the case of aerosol spray anti-seize, it is advisable to follow the instructions provided on the can as well as the Technical Data Sheet. By doing so, a consistent and even layer of anti-seize can be achieved on the surfaces of the components.
By adhering to these application guidelines, engineers and technicians can ensure proper and effective utilisation of anti-seize, enhancing its performance and maximising its protective properties on the surfaces of the assembly.
What Are the Surface Preparation Steps?
To ensure optimal results, preparing the surfaces before applying anti-seize is crucial. The following steps are recommended:
- Cleanliness: The surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from oil, grease, or contamination. Use a residue-free industrial cleaner to achieve the desired level of cleanliness.
- Removal of Oil: It is common for nuts and bolts to be supplied with a protective oil coating to prevent corrosion during storage. However, it is essential to remove this oil before applying anti-seize. Any residual oil can affect the frictional properties of the anti-seize, subsequently impacting the bolt tension and corrosion resistance.

By adhering to these preparatory measures, engineers and technicians can ensure that the surfaces are properly cleaned and primed for anti-seize application. This will enhance the effectiveness of the anti-seize and promote its ability to prevent galling, seizing, and corrosion while providing smooth assembly and disassembly.
Is It Necessary to Reapply Anti-Seize Compound?
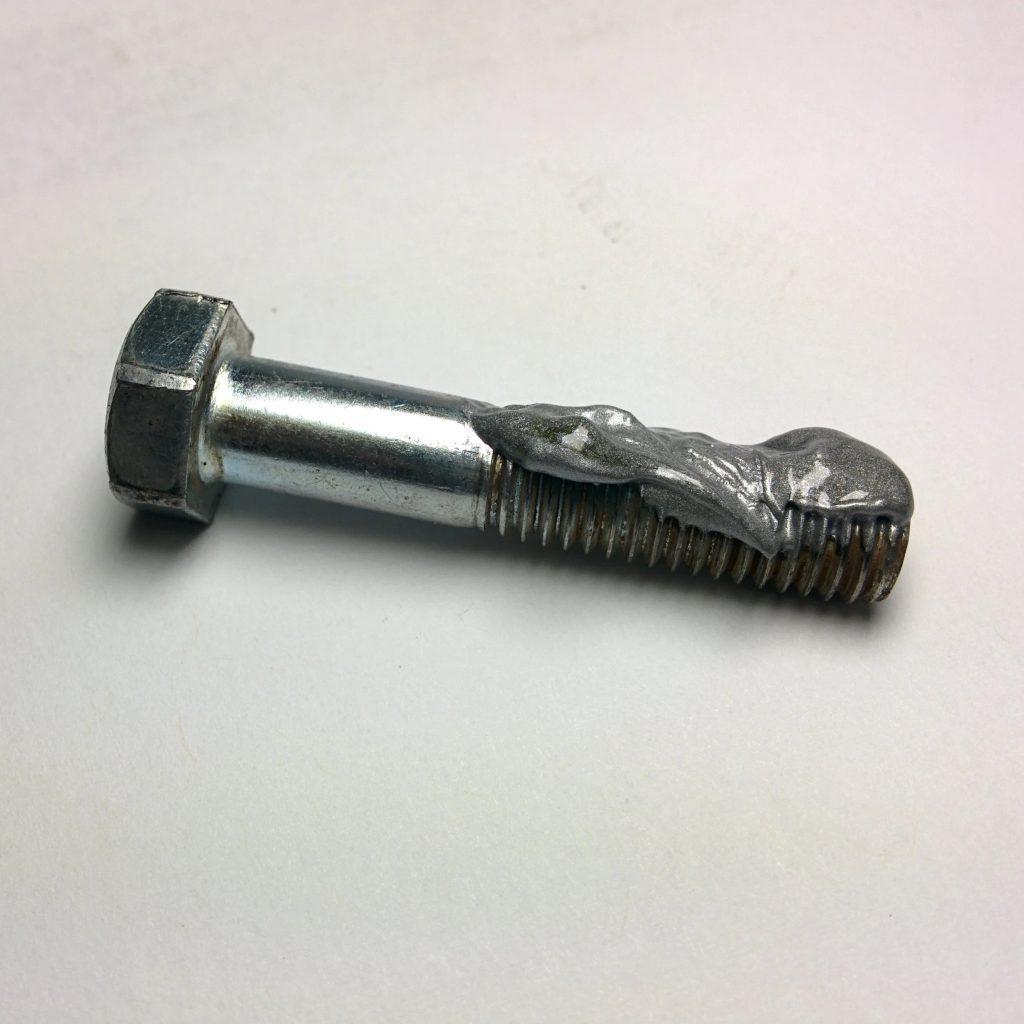

Unlike bearing grease or gearbox oil, the anti-seize compound does not require periodic replacement. Once applied, it is designed to last for the service interval of the interface, providing long-lasting protection and lubrication.
However, cleaning the components thoroughly and reapplying anti-seize is recommended when a fastener is disassembled or an interface is separated. This ensures that the surfaces remain adequately protected and lubricated during subsequent use.
When reusing or re-tightening fasteners, it is vital to exercise caution when selecting torque settings. The surfaces of fasteners undergo deformation under load, leading to potential changes in the coefficient of friction. This means the frictional characteristics may differ during subsequent uses, affecting the final tension achieved. It is advisable to consider these factors and adjust torque settings accordingly to maintain the desired performance and integrity of the assembly.
By following these guidelines and reapplying anti-seize when necessary, engineers and technicians can ensure continued protection and optimal performance of the interfaces over time.
What Are the Recommended Method for Removal?
A standard industrial degreaser or solvent cleaner is typically effective in removing an anti-seize compound from a component. Using a brush or a rag during the cleaning process is sufficient, while abrasive materials should be avoided as they can damage the surfaces of the components.
When removing the anti-seize compound, it is important to consider the subsequent stage of the component’s life:
- If a clean surface is required afterwards, it is advisable to use a residue-free cleaner. This ensures that no traces of the anti-seize or the cleaning agent remain, leaving the surface in an optimal condition for the next steps in the assembly or maintenance process.
- If the component is going to be stored, it may be necessary to apply a corrosion inhibitor to protect the surface from potential corrosion during storage. This additional step helps safeguard the component’s integrity until it is ready for use again.
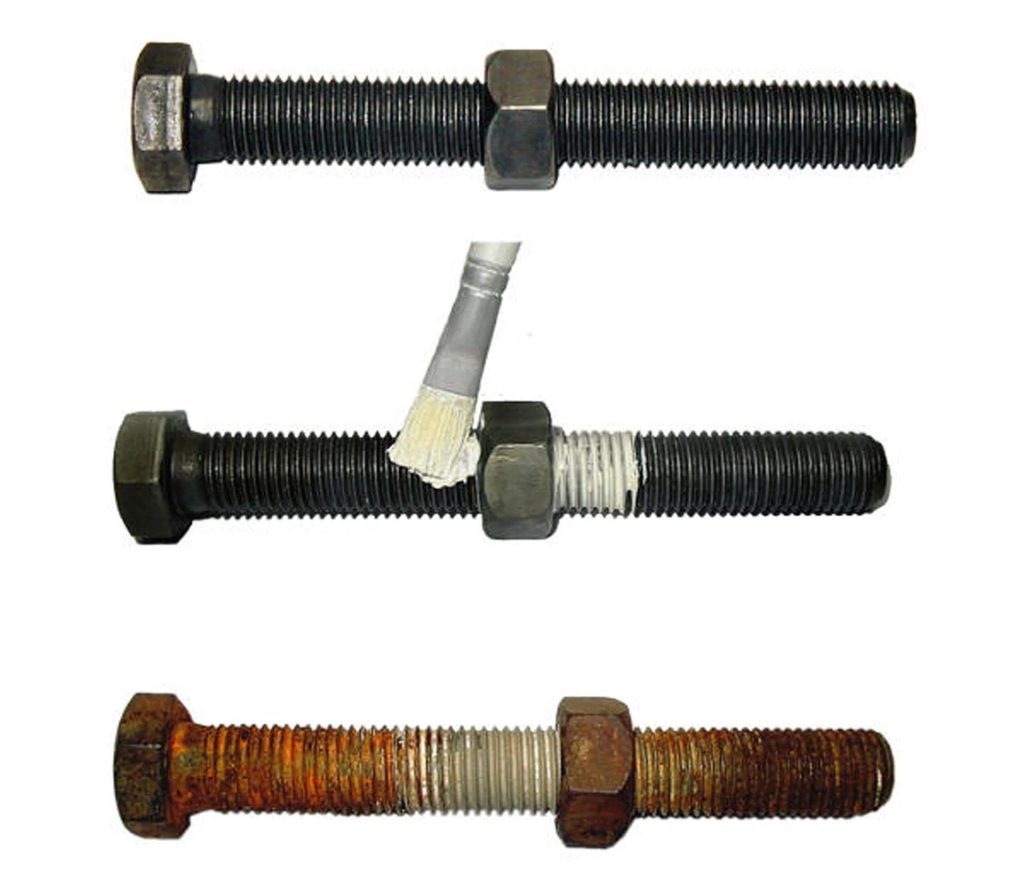

By employing these recommended cleaning practices, engineers and technicians can effectively remove anti-seize compounds from surfaces while ensuring the component is prepared appropriately for subsequent use or storage.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
Conclusion: What Is Anti-Seize Compound
In conclusion, anti-seize products are essential for mechanical assemblies and fastening systems, providing crucial protection against galling, seizing, and corrosion. By selecting and applying the right product correctly, engineers and technicians can ensure smooth operations, easy disassembly, and extended component lifespan. This comprehensive guide has covered the concept of anti-seize, its various forms, and the importance of choosing the appropriate compound for specific systems. We have explored the benefits of anti-seize, including preventing pick-up and galling, achieving precise clamping loads, reducing wear and corrosion, and facilitating disassembly. Proper surface preparation, optimal application techniques, and reapplication when necessary are key to maximising the effectiveness of anti-seize. By following these guidelines and best practices, professionals can safeguard the integrity, reliability, and longevity of clamped interfaces in mechanical systems.