In an industry increasingly relying on automation, plants and facilities need to recognise the importance of predictive maintenance in balancing their books and take the necessary steps to prioritise the maintenance of their machines. Specifically, in linear motion technology, it is crucial to ensure proper and timely lubrication for linear bearings, as with all bearings, to minimise unscheduled downtime. Investing in the maintenance of your linear bearings can lead to higher returns in the long run. To assist with this, we have compiled a list of the four most common mistakes and how to establish proper maintenance procedures for your linear bearings.
5 Common Mistakes in Maintaining Linear Bearings

Inadequate or improper lubrication is one of the main causes of failures in linear motion technology. Proper lubrication of linear bearings is essential for prolonging their lifespan and performance, significantly impacting your facility’s output.
Mistake 1: Under-Lubricating Your Linear Bearings
Mistake 2: Over-Lubricating Your Linear Bearings
Mistake 3: Incorrect Choice of Lubrication

ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
CT 609 is a very high-quality translucent grease designed for use in the food and food-processing industries.
CT 609 complies with NSF H1 and INS H1 standards for unintentional contact with foodstuffs. It contains no toxic substances, is hypoallergenic, and possesses high mechanical stability and good thermal stability.
CT 609 bonds well, is infusible (no drop point), and can be used by centralized lubrication systems.
Mistake 4: Inadequate Maintenance
Mistake 5: Neglecting Environmental Factors
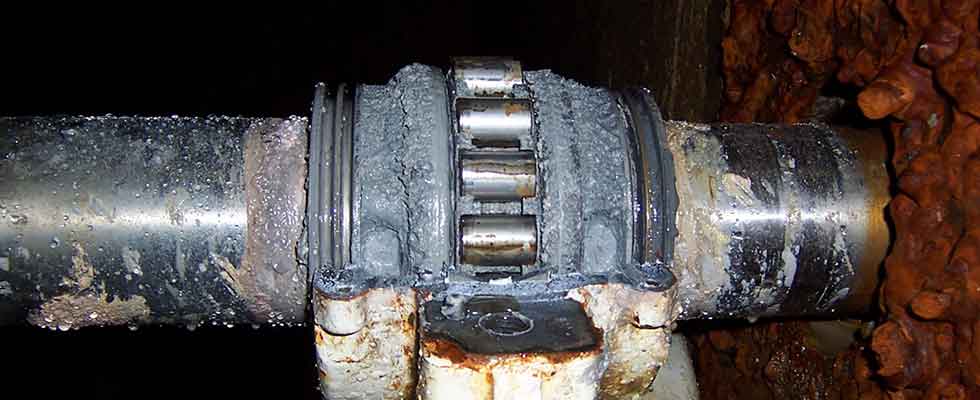

Failure to consider the operating environment can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of linear bearings, leading to unexpected failures and increased maintenance costs. Environmental conditions such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, and chemical exposure can affect linear bearings. Neglecting these factors can result in improper bearing selection or inadequate protective measures.
Temperature Extremes
High temperatures break down lubricants, causing more friction. Low temperatures thicken lubricants, affecting smooth movement. Use bearings and lubricants suited to your application’s temperature range.
Humidity and Moisture
Exposure to moisture and high humidity can cause corrosion and rust, impacting bearing performance. Bearings in such environments should be made from corrosion-resistant materials and properly sealed to prevent moisture ingress.
Dust and Contaminants
Operating in dusty or dirty environments can lead to more wear and potential failure in bearings. Using sealed or shielded bearings and maintaining proper cleaning routines can help mitigate this risk.
Chemical Exposure
It’s important to choose bearings and lubricants that are compatible with the chemicals present to avoid premature failure.
Vibration and Shock Loads
Bearings exposed to high vibration or shock loads must be designed to withstand these conditions to avoid damage and reduce operational life.
Linear Bearing Maintenance Tips

As previously mentioned, bearing lifespan largely depends on proper and timely maintenance. In fact, it is estimated that up to 80% of bearing failures result from issues related to lubrication. While this percentage sounds high, the maintenance process is not difficult. Many companies face challenges due to inadequate standard operating procedures (SOPs) and a lack of strategic maintenance schedules.
Step 1: Proper Pre-Cleaning
Begin by removing any remaining grease, corrosion protection coatings, and oils. This step is essential for preserving the equipment’s lifespan and preventing the introduction of unwanted contaminants.
Note: If the product comes pre-coated, this step may not be necessary, provided that the coating is very thin and compatible with your lubricants.
For best results, we suggest using cleaning solvents that do not leave any residue.
Step 2: Ensure Correct Fill Quantities
Step 3: Calculate Bearing Free Space
Determining the appropriate amount of lubricant to be used in a bearing is known as the Calculation of Bearing Free Space. This involves specifying the lubricant as a percentage of the bearing’s free space according to industrial standards. This critical step ensures the longevity and optimal performance of the bearing by preventing over-lubrication or under-lubrication.
The exact fill quantities can be obtained through direct communication with the bearing manufacturer via a phone call or email, which provides precise and tailored information. Alternatively, a grease calculator can be used to estimate the required lubricant amount. However, it should be noted that this method has limitations in accuracy and may not be as reliable as consulting the manufacturer directly.
Step 4: Run-In Procedures
- Grease the linear bearing elements to form a grease collar, ensuring an even distribution of the base oil where friction surfaces receive the optimal oil quantity.
- Purge any leftover grease from your system.
- Create a grease collar to deliver oil to the surface contact zone.
- Let the system cool down to room temperature.
- Restart the procedure at the last speed prior to the temperature spike.
- Continue the above cycle until the maximum operating speed is achieved.
Step 5: Lubricating Your Bearings
Lubricate your linear bearings in a dry and clean environment to minimise contamination from moisture or debris. For smaller amounts, use a calibrated grease gun or a syringe. Rotate the bearings without load to distribute the grease evenly through the race.
Conclusion
Remember, proper maintenance of linear bearings is essential for equipment performance and lifespan. Balance lubrication and select suitable lubricants to reduce downtime and costs. Use a mix of preventive and predictive maintenance to enhance efficiency and profitability in operations involving linear motion technology.