Nonfood Compounds Registration (NCR)
Nonfood Compounds Registration (NCR) is a program offered by NSF International that provides third-party certification and testing services. The NCR program provides independent certification for proprietary substances and nonfood compounds, such as lubricants, cleaners, and other chemicals used in the food and beverage industry.
The NCR program evaluates proprietary substances and nonfood compounds against a set of rigorous standards for product formulation, manufacturing, labelling, and packaging. If a proprietary substance or a nonfood compound meets these standards, it is awarded certification, which provides assurance to food and beverage manufacturers and processors that the compound is safe and can be used in their facilities without the risk of contaminating food products.
Nonfood Compounds vs. Proprietary Substances
Nonfood compounds and proprietary substances are both regulated by NSF International, but they differ in their definitions and uses. While both nonfood compounds and proprietary substances are subject to regulation by NSF International, they have different criteria for their evaluation and certification. Nonfood compounds are evaluated based on their nonfood contact use, while proprietary substances are assessed based on their direct food contact use.

Nonfood Compounds
Nonfood compounds are chemicals used in food processing establishments but are not intended to come into direct contact with food. These may include cleaning and sanitising agents, lubricants, and pest control substances.
Proprietary Substances
On the other hand, proprietary substances are chemicals that are used in food processing and are intended to come into direct contact with food. These may include food packaging materials, processing aids, and ingredients.
NSF Certification Limits for Food Safety
The NSF certification only indicates that the product has undergone testing and meets the standards set by the NSF for a specific category. Therefore, there could still be potential risks associated with the use of the product in the food and beverage industry that the NSF testing has not identified.
Nonfood Compounds

NSF evaluates and certifies nonfood compounds, substances used in food processing facilities that do not come into direct contact with food. The certification process involves assessing the ingredients and manufacturing process of these substances to ensure that they do not pose a health risk to humans when used in accordance with their intended use and labelled instructions.
So why is the NSF certification necessary for nonfood compounds? Because it does provide an additional level of assurance that nonfood compounds are manufactured and formulated in a way that minimises the risk of contamination and adverse health effects. Still, NSF certification does not guarantee that a product is food safe.
Proprietary Substances
NSF evaluates the safety of proprietary substances based on their formulation, intended use, and potential exposure to food. However, the certification may not account for all potential factors that could affect the safety of the final product. For example, the concentration and purity of the product, as well as how it is used and handled, can all impact its safety. Additionally, certain products may not be safe for use with certain types of food or in certain processing or handling conditions.

Ensuring Food Safety for Chemical Products
Ensuring the safety of chemical products used in the food and beverage industry is crucial. However, ORAPI goes beyond NSF certification and takes the following additional steps to guarantee the safety of our products:

- We provide complete transparency regarding our product information. This includes featuring NSF codes on the Technical Data Sheets (TDS) and labels of all our products.
- The NSF Whitebook allows for verification of both the NSF certifications and expiration dates of our products.
- We state the appropriate concentration and purity of our products as well as create food-grade products that are safe for use on food surfaces.
- To ensure compatibility with food contact surfaces, we also conduct our own testing and analysis. Following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and implementing Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) programs are some additional measures we take to ensure the safety and quality of our products.
- We also engage Third-party certification organisations such as Halal and ISO for regular audits to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Understanding NSF Codes
NSF uses category codes to classify various proprietary substances and nonfood compounds. To determine whether ORAPI’s products containing nonfood compounds are NSF certified, go to nsfwhitebook.org and search for “ORAPI” under Company Name. On the far-left column, you will find a list of all our NSF-certified products, along with their respective category codes. If you want to know the meaning of each category code, simply click on it, and you’ll be redirected to a list that outlines all the codes and their respective labels.

To determine whether products with a particular category code can be safely used in food processing areas, select a product that corresponds to the category you’re interested in. The text in bold will indicate how products in that specific category can be safely used in food processing areas.
Steps to Validate NSF Certificate
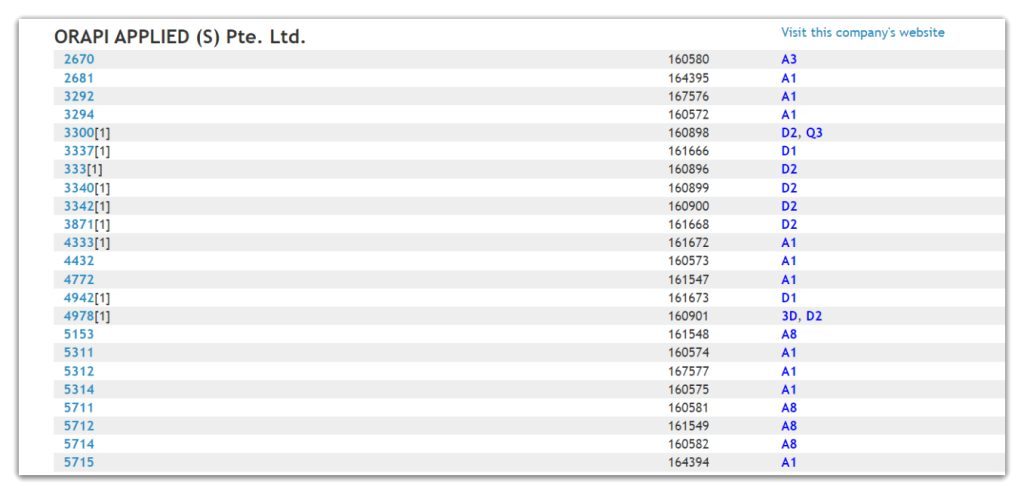
Let’s use an example to illustrate how you can obtain an NSF certificate for a particular product that corresponds to a specific category:
For example, if you’re interested in knowing whether products in the D1 category (antimicrobial agents requiring a rinse) can be safely used in food processing areas, follow these steps:
- Visit nsfwhitebook.org and search “ORAPI.”
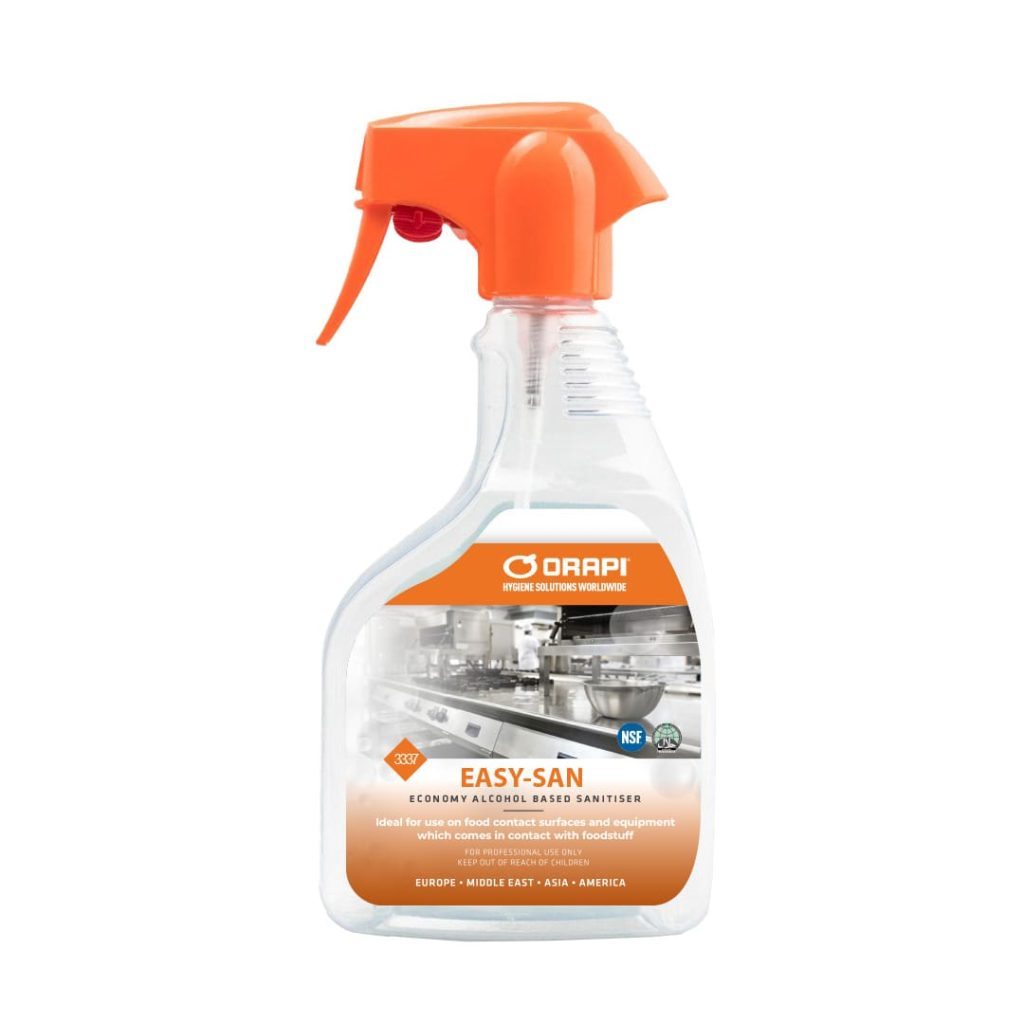
- Press Ctrl+F to locate product 3337 and verify whether its category code is D1.
- Click on the product code 3337 to view the NSF certificate specifically issued for that product.
- Alternatively, click on the category code D1 to confirm whether that is the code you are searching for.
- Look for the bolded text that reads:

Now you know that products in the D1 category require a rinse to be used as a sanitizer in and around food processing areas.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
Some Common Category Codes
Below we have mentioned some common category codes and a description of how the products can be used safely in and around food processing areas (retrieved directly from the NSF certificates on nsfwhitebook.org).
Please note that the Safety column provides only brief snippets of precautions. To access the entire bolded text, please refer to the instructions above for retrieving the relevant NSF certificate.
|
Category Code |
Description |
Safety |
Product Code |
|
A1 |
General Cleaners |
“This product is acceptable for use as a general cleaner (A1) on all surfaces in and around food processing areas, where its use is not intended for direct food contact.” |
2681 |
|
D2 |
Antimicrobial agents not requiring rinse |
“This product is acceptable for use as a sanitizer on all surfaces not always requiring a rinse (D2) in and around food processing areas.” |
3340 |
|
A8 |
Degreasers/carbon removers |
“This product is acceptable as a degreaser or carbon remover for food cooking or smoking equipment, utensils, or other associated surfaces (A8) in and around food processing areas, where its use is not intended for direct food contact.” |
5711 |
Conclusion
NSF International certifies nonfood compounds for the food and beverage industry, but its certification doesn’t guarantee complete safety. However, at ORAPI, by maintaining full transparency by stating our category codes on labels and TDS and taking extra measures to ensure the safety and quality of our products, we go beyond NSF certification for product safety. Therefore, understanding NSF codes and the method of retrieving certification is essential to know how each nonfood compound can be used safely in food processing. To learn more about where we can help you, click the button below.