EP grease with Extreme-Pressure (EP) additives are highly advanced greases designed to provide lubrication, protection, and sealing for machine components and heavy-duty applications that require an Extreme-Pressure semisolid lubricant.
Greases without EP additives may struggle or fail to meet the demands of heavy-duty tasks, such as the lubrication of heavily loaded bearings. Extreme-Pressure additives offer excellent protection for machine components and vehicles operating under extreme conditions, providing increased resistance to rust, oxidation, and improved shear stability compared to non-EP greases.
Extreme-pressure greases typically outperform basic greases in all areas, with some formulations better suited to specific applications like high-load, moisture-heavy, or high-speed machine operations.
What is EP Grease?

Extreme Pressure” (EP) grease is specifically made to lubricate machine components in environments with heavy shock loading and high pressures. Non-EP greases are not suitable for these conditions as they cannot adequately provide lubrication between the machine’s surfaces. In contrast, EP greases consistently offer a lubricating layer in high-pressure situations, which helps reduce machine wear and optimize performance.
Composition of EP Greases

EP greases are heavy-duty greases that have been improved with extreme pressure additives. These additives, such as graphite and moly, enhance the performance of the grease by bonding to the metal surfaces of machine components and providing an additional barrier between surfaces.
Composition of EP Greases
EP grease is composed of base oils, which can be mineral, synthetic, or a blend of both. These base oils are crucial for the overall performance and suitability of the grease for various applications. The common additives used in EP grease include sulfur-phosphorus compounds and molybdenum disulfide. These additives function to enhance performance under extreme pressures by creating a protective film on metal surfaces, reducing friction, and preventing wear even under high load and shock load conditions.
EP Grease Applications

As mentioned, EP greases are designed to withstand heavy shock load and extreme pressure applications. They can be used in universal joints, chassis points, slide and cam mechanisms, bearings, etc. Typically, EP greases can work in a wide range of temperatures, with most boasting a higher dropping point than standard greases.
Industrial Uses
EP grease is essential in manufacturing, mining, and construction industries, where machinery operates under high load and severe conditions.
Automotive Applications
EP grease is commonly used in wheel bearings, chassis components, and other automotive parts that experience significant friction and pressure.
Specific Machinery and Equipment
Various types of machinery, such as cranes, excavators, and heavy-duty equipment, benefit from the protective properties of EP grease, ensuring longevity and optimal performance.
Advantages of EP Grease

Extreme Pressure Resistance
The primary role of EP grease is to prevent metal machine components from rubbing directly against each other. Without this separation, these components can generate damaging debris and sometimes even weld together. EP greases effectively prevent such occurrences. In contrast, conventional greases may fail under extreme pressure or high shock loads, allowing metal-to-metal contact.
Water Resistance
EP greases, unless specifically designed for water resistance, can experience a loss of their enhanced lubricating effectiveness when exposed to water. This susceptibility can lead to “wash-out,” where essential additives separate from the grease, rendering it ineffective. Additionally, water presence within machinery can accelerate corrosion. Water-resistant EP grease helps mitigate these risks by slowing down the corrosion process. Greases formulated with simple soap thickeners are particularly vulnerable to wash-out. Therefore, EP greases that utilize complex soap thickeners are often preferred for environments where moisture is a concern. Specifically, greases employing lithium complex thickeners are versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications.
Increased Equipment Lifespan
EP grease plays a pivotal role in increasing equipment lifespan and reducing maintenance costs due to its superior lubrication capabilities under extreme pressure conditions. By forming a durable film between metal surfaces, EP grease minimizes friction and wear, thereby prolonging the life of critical components such as bearings, gears, and sliding mechanisms. This reduction in friction also translates to lower energy consumption and operational temperatures, further enhancing the efficiency of machinery. As a result, maintenance intervals can be extended, downtime reduced, and overall operational costs minimized, making EP grease a cost-effective solution for industries reliant on high-performance equipment.
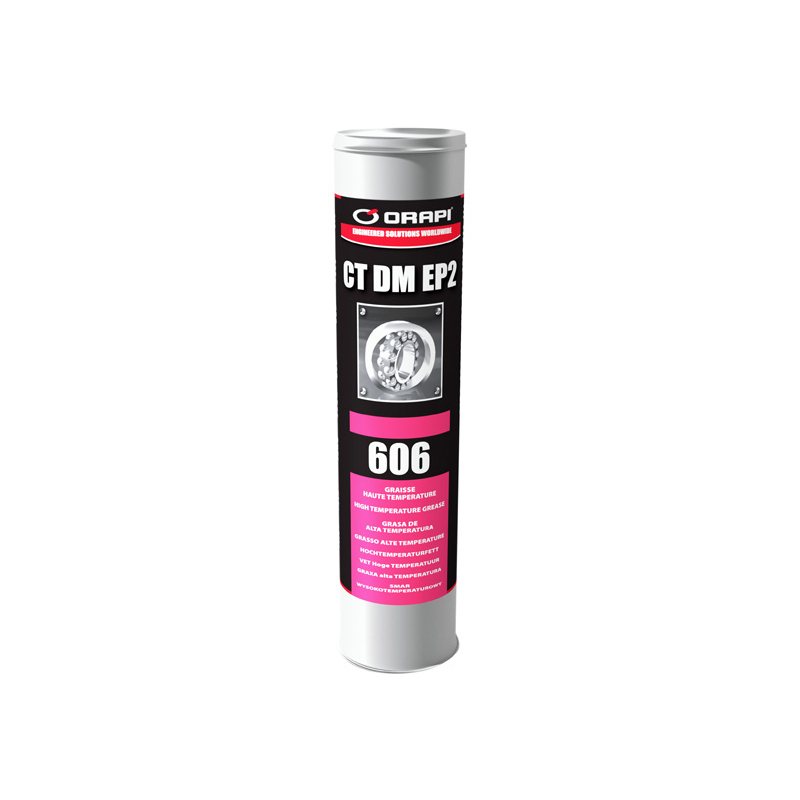
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
CTDMEP 2 is a high performance semi-synthetic grease, formulated to serve the most severe demanding requirement of equipment and machineries operating at high temperatures and high speed under corrosive atmospheres. CTDMEP 2 is recommended for use in refineries, chemical and petrochemical industries, paper mills and steel mills, textile industries.
Types of EP Grease
EP greases come in various formulations tailored to specific applications and operating conditions. The types of EP grease can be classified based on several factors, including their base oil type, thickener composition, and the specific additives used. Here are some common types:
Mineral Oil-Based EP Grease
These greases use mineral oil as the base fluid, providing good lubrication properties across a wide temperature range. They are cost-effective and suitable for general-purpose applications where extreme pressure resistance is required.
Synthetic Oil-Based EP Grease
Synthetic oil-based EP greases have synthetic base oils (such as polyalphaolefin (PAO), esters, or polyalkylene glycols), offering superior performance in extreme temperatures, high speeds, or harsh environments. They provide enhanced oxidation resistance and longer service life compared to mineral oil-based greases.
Calcium Sulfonate Complex EP Grease
This type of EP grease uses a calcium sulfonate complex thickener, which provides excellent water resistance, corrosion protection, and high temperature stability. They are often used in marine applications, steel mills, and other heavy industrial environments.
Lithium Complex EP Grease
Lithium complex greases combine lithium soap with complexing agents to improve thermal stability, water resistance, and mechanical stability under heavy loads. They are versatile and find applications in automotive, construction, and agricultural equipment.
Aluminum Complex EP Grease
Aluminum complex greases offer high water resistance, excellent adhesion to metal surfaces, and good compatibility with plastics and elastomers. They are commonly used in food processing equipment, pharmaceuticals, and other industries requiring NSF H1 certified lubricants.
Polyurea EP Grease
Polyurea-based greases use polyurea as the thickening agent, providing exceptional high-temperature stability and mechanical stability under high-speed conditions. They are often used in electric motors, sealed-for-life applications, and in areas requiring long lubrication intervals.
Bentonite Clay EP Grease
Bentonite clay greases are characterized by their high dropping point and resistance to water washout. They are used in high-temperature applications where conventional greases may fail.
Relationship Between EP and NLGI Grade

NLGI (National Lubricating Grease Institute) grade is a measure of the consistency or thickness of grease. It categorizes greases into different grades based on their penetration value, which indicates how soft or stiff the grease is. The NLGI grade is typically represented by numbers ranging from 000 (very soft) to 6 (very stiff).
The relationship between EP greases and NLGI grade lies in how the consistency of the grease affects its performance in different applications
NLGI Grade and Application Suitability
Lower NLGI Grades (000 to 1)
These greases are softer and have a higher penetration value. They are suitable for applications where low viscosity and easy pumpability are required, such as in centralized lubrication systems or in cold weather conditions.
Medium NLGI Grades (2 to 3)
Greases in these grades have a moderate consistency and are the most commonly used in industrial applications. They provide good stability and pumpability over a wide range of operating conditions, making them versatile for general-purpose lubrication.
Higher NLGI Grades (4 to 6)
These greases are stiffer and have a lower penetration value. They are used in applications where resistance to leakage, vibration, and high mechanical stability under heavy loads are critical, such as in heavy industrial machinery and bearings.
EP Additives and NLGI Grade
EP additives can affect the NLGI grade of grease by influencing its thickening ability and consistency. For example, greases with EP additives may require specific thickener systems to maintain their desired NLGI grade while ensuring effective extreme pressure protection.
Choosing the Right NLGI Grade for EP Greases
The selection of NLGI grade for EP greases depends on the application requirements, such as operating temperatures, speed, load conditions, and environmental factors. It is essential to choose a NLGI grade that ensures proper lubrication film thickness and mechanical stability under the specific operating conditions to maximize equipment performance and longevity.
Testing and Grading of EP Greases
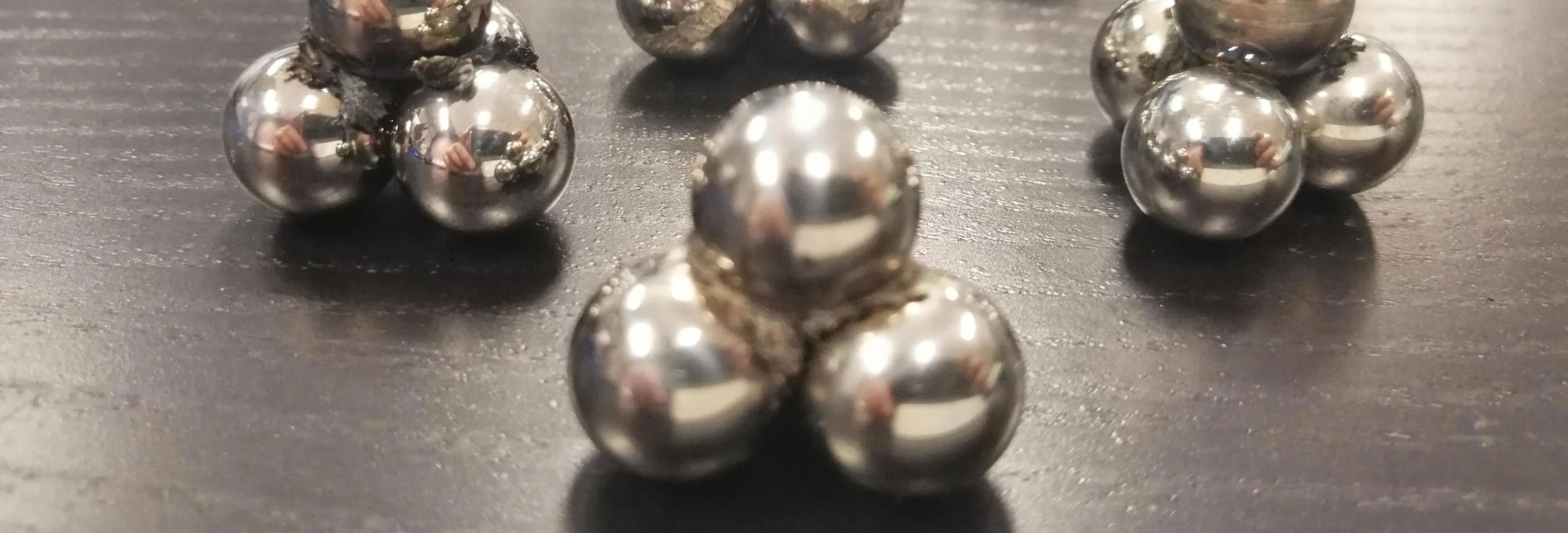

Greases undergo rigorous testing to assess their performance under various conditions. The ASTM D-1264 Water Washout Test evaluates water resistance, while pressure-handling abilities are measured using ASTM methods such as D-2596 (Four-Ball Weld Test) or D-2509 (Timken OK Load Test). These tests provide crucial data for comparing different EP greases.
In the Four-Ball Weld Test, four ball bearings are immersed in the grease being tested, with one ball allowed to rotate. The test involves gradually increasing the load until welding occurs between the balls. Welding indicates severe friction and heat between metal surfaces, causing them to adhere together. A welding load exceeding 250 kg classifies the grease as “Extreme Pressure Grease,” indicating superior pressure-handling capabilities. A welding load of 160 kg categorizes the grease as “Normal Grease.”
Additionally, greases are categorized based on their consistency using the NLGI grading system established by the National Lubricating Grease Institute. Greases receive an NLGI grade, with lower grades indicating less viscosity. For instance, most industrial lubricating greases have an NLGI grade of 2, indicating moderate viscosity suitable for general-purpose applications.
Conclusion
Extreme-Pressure (EP) greases are crucial for high-performance lubrication in demanding conditions. Enhanced with EP additives, these greases provide superior protection against wear, rust, and oxidation, ensuring machinery longevity and efficiency in automotive and heavy industrial use. Selecting the right EP grease type and NLGI grade for specific applications optimizes machinery operation, extends maintenance intervals, and reduces operational costs.