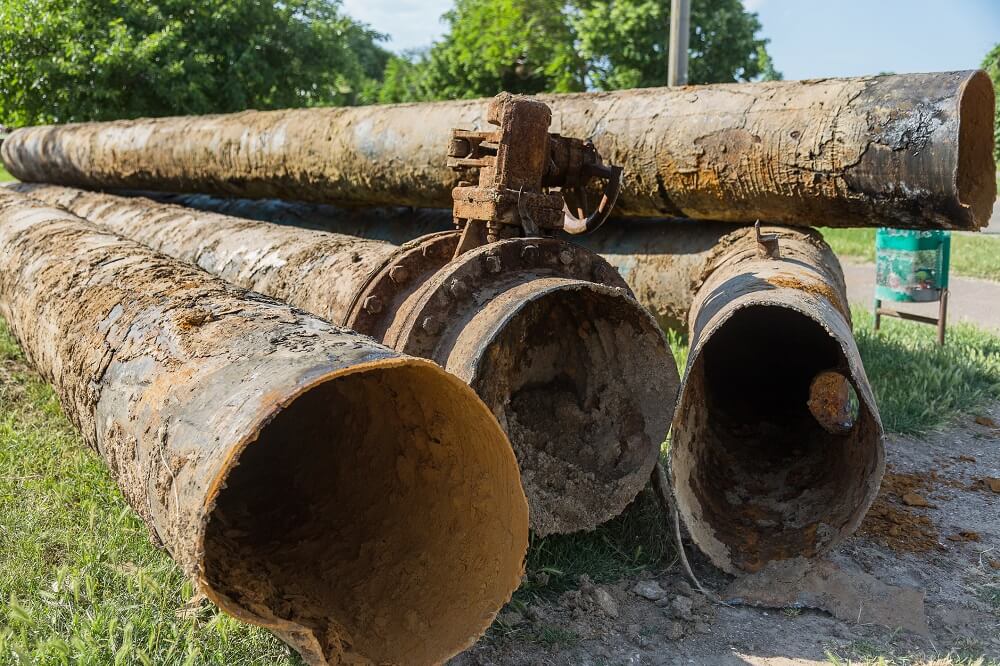
What Causes Pipe Corrosion?
1. Be Mindful of Water Usage With Pipes

To prevent corrosion, it’s important to maintain a proper pH level in copper piping, as water is a major cause of such damage. The EPA recommends keeping the pH of your water between 6.5 and 8.5.
It’s also important to monitor oxygen levels in your water, as it can lead to rust and blockages. To minimise the risk of corrosion, try to keep the water temperature low whenever possible, as hotter water has a higher tendency to cause damage.
2. Maintain Clean Pipes

Corrosive bacteria can cause microbiologically induced corrosion (MIC) when metals are exposed to them. To prevent MIC, it is advisable to keep the pipes clean, especially when they come in contact with sulphides regularly. One can use biocides or inhibitors to keep fluids clean. Alternatively, chemical treatment for water or other liquids can also be considered.
3. Apply Protective Coating to Metal Surfaces

Preventing corrosion is crucial for the longevity and safety of pipes and other surfaces. One effective method is to apply protective linings or special coatings. This can include galvanisation, which adds a layer of zinc to metallic surfaces like steel or iron. Additionally, using a sealant can help keep corrosive bacteria from settling into joints or crevices, further reducing the risk of corrosion.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
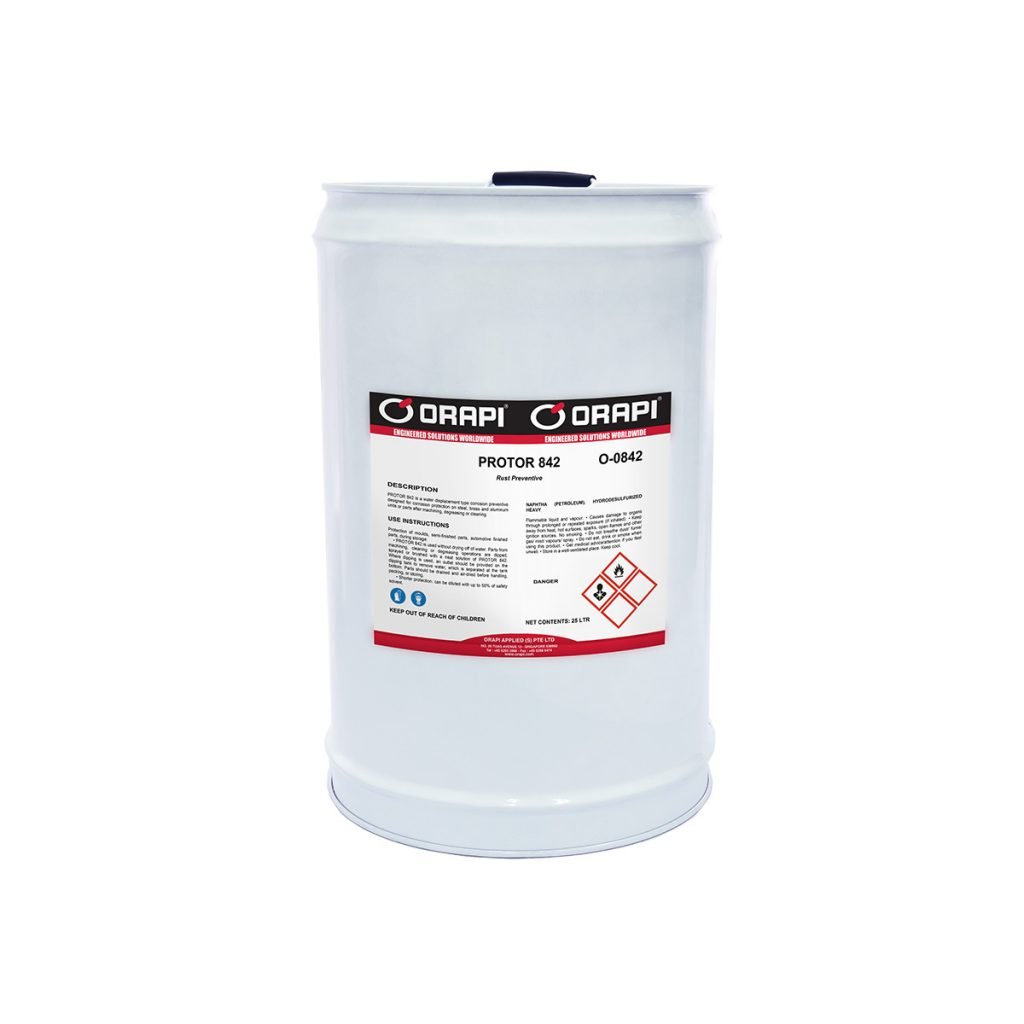
PROTOR 842 serves as a water displacement corrosion inhibitor, specifically formulated to safeguard steel, brass, and aluminum components or assemblies after machining, degreasing, or cleaning, providing effective corrosion protection.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
- Anti-corrosion, water-repellent protective product that produces a semi-greasy film. (Available in red 804 and colourless 791).
- In the workshop, PROTOR SG 100 is designed to protect parts awaiting machining, final packaging or surface treatment.
- Protects tools and injection moulds.
- Storage between machining operations or long-term storage.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
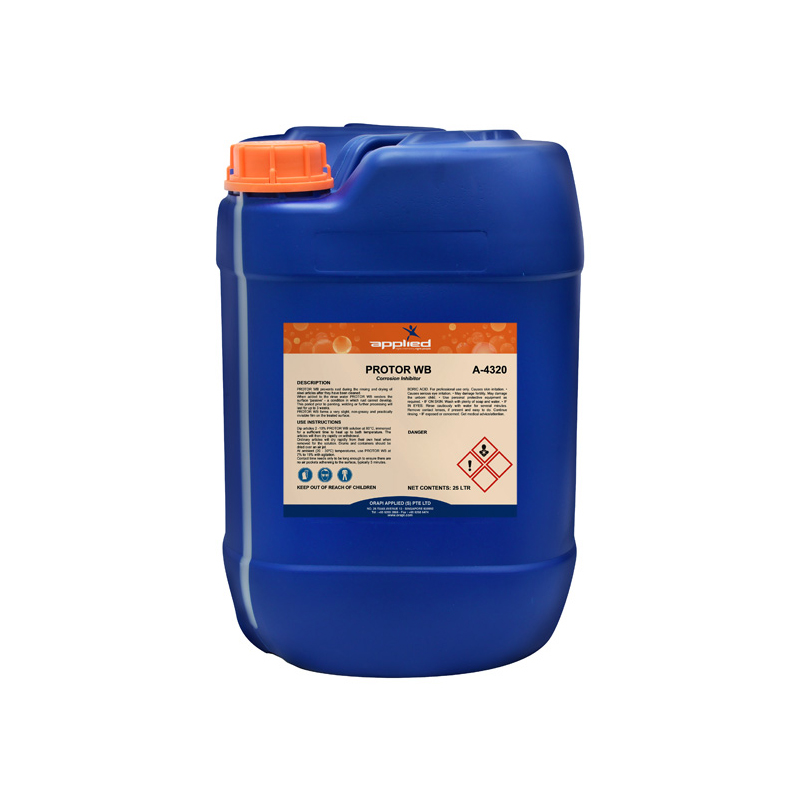
PROTOR WB (formerly known as A-4320) shields steel articles from rust formation during the rinsing and drying process post-cleaning. Its incorporation into the rinse water induces a ‘passive’ state on the surface, preventing the onset of rust. This protective phase, enduring for up to 3 weeks, facilitates subsequent procedures such as painting, welding, or further processing.
4. Maintain Structural Stability

5. Prevent Direct Contact Between Metals

Conclusion: Prevent Pipe Corrosion
In a world where the financial toll of corrosion stands at a staggering $2.5 trillion, the threat posed by pipe corrosion looms large, potentially causing production downtime, workplace hazards, and substantial financial losses. However, understanding the causes and employing preventive measures against corrosion offers hope. By maintaining optimal water conditions, using protective coatings, keeping pipes clean, ensuring structural stability, and preventing direct metal contact, corrosion can be mitigated effectively. Embracing these methods safeguards pipes, secures budgets, and enhances safety. With proactive measures and informed strategies, the battle against pipe corrosion can be won, ensuring the resilience and longevity of vital infrastructure.