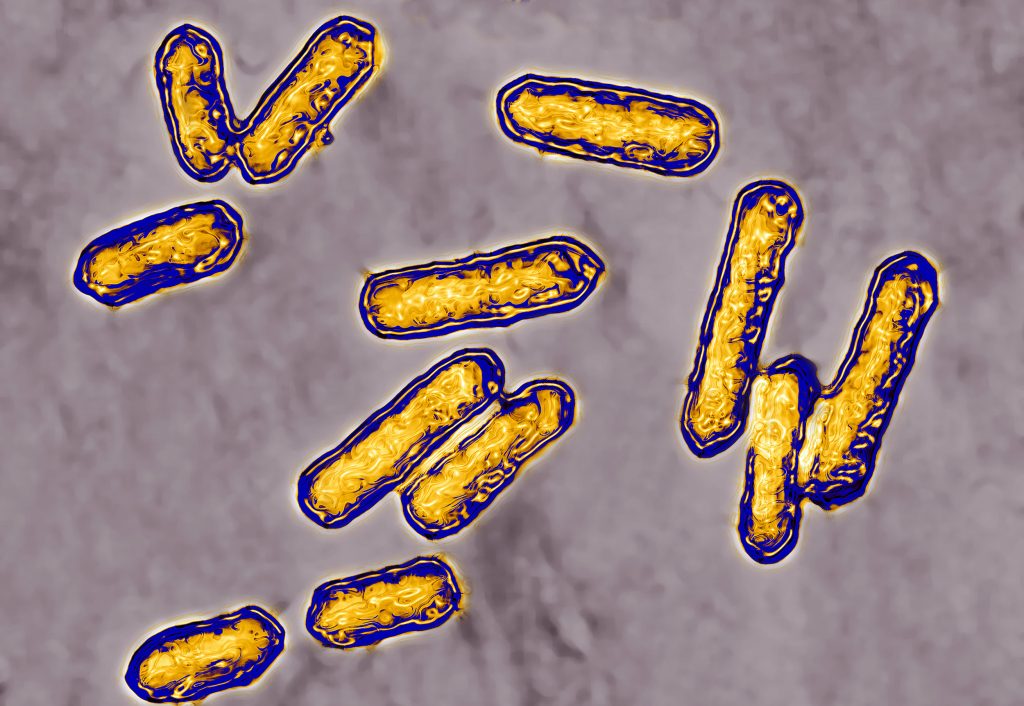
Listeria monocytogenes is a type of bacteria that can cause listeriosis, a foodborne illness in humans. These bacteria are Gram-positive, facultative intracellular pathogens commonly found in animals, soil, and water sources, which can contaminate dairy products and produce. Furthermore, ready-to-eat meat products may also become infected with L. monocytogenes due to the formation of biofilms on food processing equipment.
If a person ingests food contaminated with L. monocytogenes, they may develop a potentially serious illness known as listeriosis. The transmission of L. monocytogenes can occur during several stages of food processing, such as harvesting, processing, preparation, packaging, transportation, or storage, in environments contaminated with L. monocytogenes.
Symptoms of Listeriosis
Listeriosis can produce a range of symptoms, and the severity of the illness can vary. Mild symptoms may include fever, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea. However, more severe forms of listeriosis can lead to headaches, stiff neck, confusion, loss of balance, and convulsions. For vulnerable populations, such as the very young, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems, listeriosis can be fatal.
Survival of Listeria
Listeria are rod-shaped bacteria that exist in various environmental sources, including soil, water, effluent, and human and animal faeces. They can adapt to diverse ecological conditions, such as temperature, low pH, and high salt concentrations. For example:
- Listeria can grow in temperatures ranging from -1°C to 45°C, making it capable of surviving in refrigerated environments. However, temperatures above 50°C can kill it. This implies that Listeria can thrive and proliferate even in cold storage, such as refrigerators.
- The bacteria can also survive with or without oxygen, which allows it to thrive in vacuum-sealed packages of cooked sausages, cold cuts, and smoked fish.
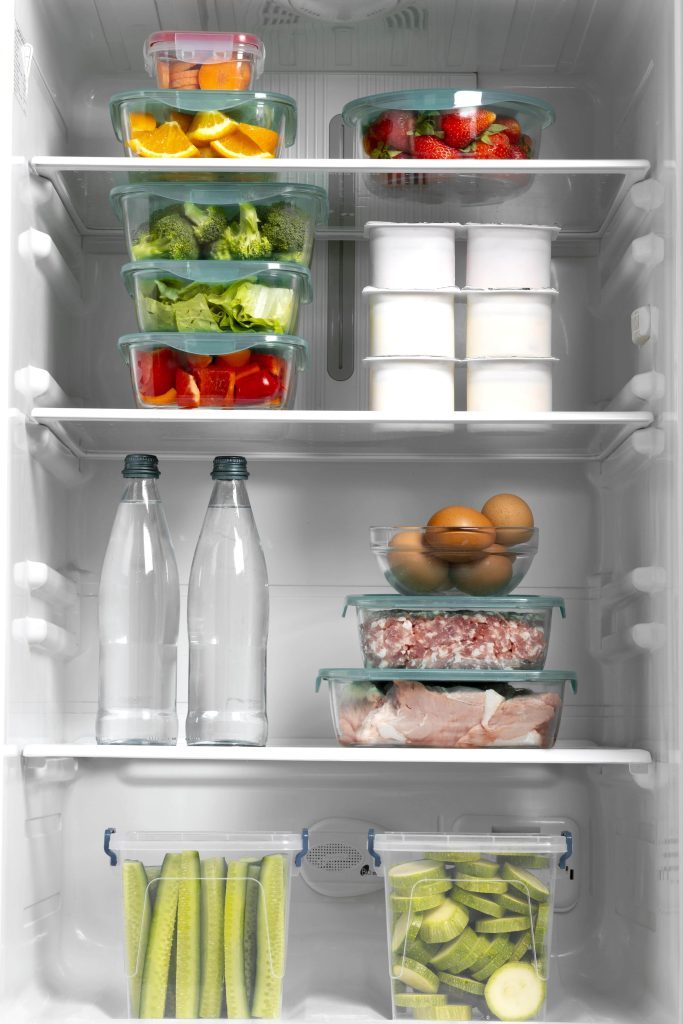

Sources of Listeria
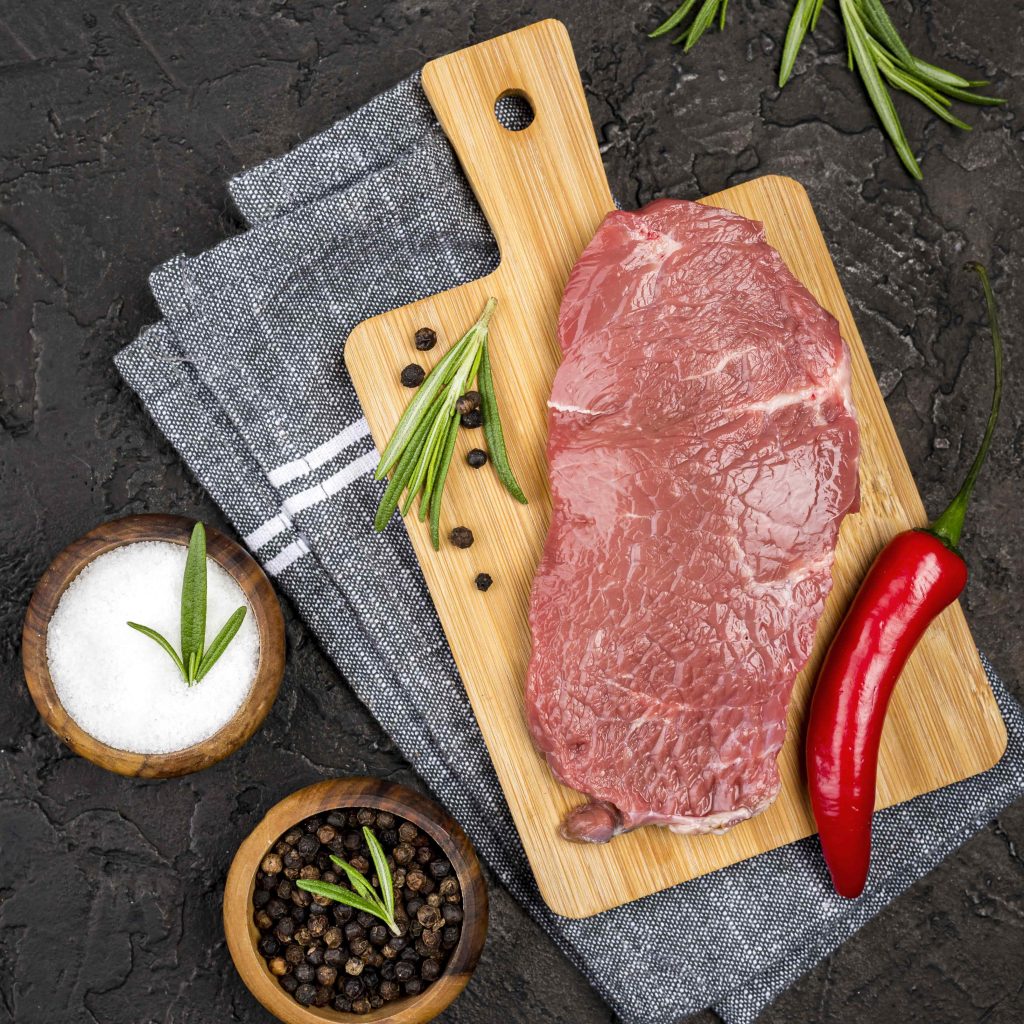

Foods that are more susceptible to Listeria contamination include:
- Deli meats and sausages that are ready to eat;
- Refrigerated meat spreads such as pâté;
- Unpasteurised (raw) dairy products, like raw goat’s milk and cheese;
- Soft cheeses that are ripened by mould, for example, B. Romadur and Roquefort; and
- Smoked fish like salmon
Survival of Listeria
Compromised Immune Functioning
Listeriosis can vary in severity, and in some cases, it can be life-threatening, particularly among certain at-risk groups with impaired immune functioning. These high-risk groups include:
- Older adults over the age of 65
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or who are undergoing chemotherapy
- Individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease
- Those taking certain medications, such as high-dose prednisone or certain drugs for rheumatoid arthritis
- Individuals who have undergone organ transplants and take medications to prevent rejection.

Pregnant Women
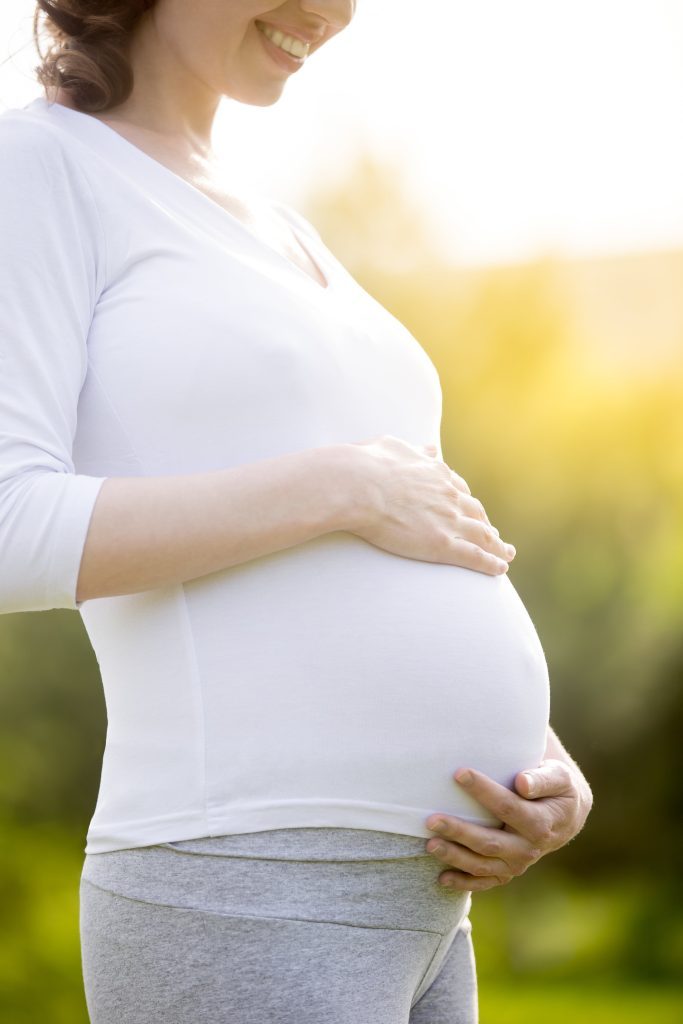

Pregnant women and their newborn babies are particularly vulnerable to the dangers of listeriosis, which can lead to serious complications during pregnancy, such as miscarriage and stillbirth. In addition, if a baby is born with a listeriosis infection, it can result in severe health complications that require urgent medical attention, potentially leading to lifelong health issues or even death.
It is crucial for pregnant women to seek immediate medical attention if they suspect they have developed symptoms of listeriosis, such as muscle aches, nausea, stiffness in the neck, or headaches, and to inform their healthcare provider about any potentially contaminated food they may have consumed. Prompt medical care can help prevent serious health consequences for the mother and the baby.
Guidelines for Restaurants and Retailers

Restaurants and retailers can take several steps to prevent the spread of Listeria and reduce the risk of contamination in their establishments. Here are some guidelines:
- Ensure proper storage and temperature control: To prevent L. monocytogenes from growing, make sure your refrigerator is set to 4°C (40°F) or below and your freezer is set to -18°C (0°F) or below.
- Clean and sanitise food contact surfaces: Clean the inside walls and shelves of your refrigerator, cutting boards, countertops, and any utensils that may have come into contact with contaminated foods. Then, sanitise them with an appropriate solution with bactericidal properties. Dry with a clean cloth or paper towel that has not been used before. Wash and sanitise display cases and surfaces where potentially contaminated foods may be stored, served, or prepared.
- Maintain personal hygiene: Always wash your hands with warm water and a potent hand wash after cleaning food contact surfaces, and make sure to have hand sanitiser readily available so you can frequently sanitise your hands throughout the day.
- Maintain proper food handling practices: Ensure that all staff members are trained in acceptable food handling practices and follow them consistently. This includes washing hands thoroughly before handling food, wearing gloves, and using clean utensils and surfaces.
For additional information on how consumers can control the spread of Listeria, follow the guidelines recommended by the Singapore Food Agency (SFA).
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
RINCON is a foaming sanitizing detergent formulated for effectively cleaning and disinfecting surfaces in food areas.
RINCON is formulated with a blend of detergents, sequestrants and quaternary ammonium compounds specially selected to be effective against a wide range of microorganisms for maximum hygiene.
DISAKLEEN is a neutral concentrated detergent & disinfectant, developed for surface cleaning applications in the food, beverage and dairy industries. It also is formulated with a blend of foaming detergents, sequestrants and quaternary ammonium compounds specially selected to be highly effective against most vegetative forms of micro-organisms including Gram-positive & Gram-negative bacteria & yeasts, and enveloped viruses**.
MANEKLINE® MDSA is an alcohol-free disinfecting foam for
hygienic treatment and disinfection of hands by rubbing.
ORAPI RECOMMENDS:
MANEKLINE® GHA is a thixotropic hydroalcoholic gel for hygienic treatment and disinfection of hands by rubbing.
MANEKLINE® GHA is recommended for use in hospitals, veterinary clinics, schools and offices, kitchens, food processing plants, manufacturing plants, or anywhere a good hygiene level is important.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Listeria monocytogenes is a type of bacteria that can cause listeriosis, a serious foodborne illness that affects vulnerable populations such as the elderly, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems. Listeria bacteria can survive and proliferate in a range of environmental conditions, including refrigerated environments, and can contaminate food at various stages of preparation and processing. Restaurants and retailers can reduce the risk of contamination by ensuring proper storage and temperature control, cleaning and sanitising food contact surfaces, and maintaining personal hygiene. Anyone who suspects they have contracted listeriosis should seek medical attention promptly to prevent serious health complications.